Abstract
Rationale
Comorbid depression is commonly observed in individuals who suffer from neuropathic pain, which necessitates improved treatment. Curcumin, a phenolic compound derived from Curcuma longa, possesses both antinociceptive and antidepressant-like activities in animal studies, suggesting its possible usefulness in treating this comorbidity.
Objective
We investigated the effect of curcumin on depressive-like behaviors in mice with mononeuropathy, and explored the mechanism(s).
Methods
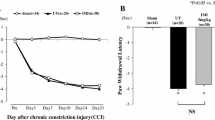
Chronic constriction injury (CCI) was produced by loosely ligating the sciatic nerves in mice. The nociceptive behaviors were examined using Hargreaves test, and the depressive-like behaviors were determined by forced swim test (FST) and tail suspension test (TST).
Results
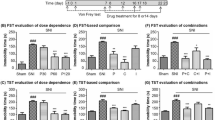
After CCI injury, the neuropathic mice developed nociceptive and depressive-like behaviors, as shown by thermal hyperalgesia in Hargreaves test and protracted immobility time in FST and TST. Chronic treatment of neuropathic mice with curcumin (45 mg/kg, p.o., twice per day for 3 weeks) corrected their exacerbated nociceptive and depressive-like behaviors, which was abolished by chemical depletion of brain serotonin rather than noradrenaline. The paralleled antinociceptive and antidepressant-like actions of curcumin seem to be pharmacologically segregated, since intrathecal and intracerebroventricular injection of methysergide, a nonselective 5-HT receptor antagonist, separately counteracted the two actions of curcumin. Further, this antidepression was abrogated by repeated co-treatment with 5-HT1A receptor antagonist WAY-100635 and greatly attenuated by acute co-treatment with GABAA receptor antagonist bicuculline.
Conclusion
Curcumin can normalize the depressive-like behaviors of neuropathic mice, which may be independent of the concurrent analgesic action and possibly mediated via the supraspinal serotonergic system and downstream GABAA receptor.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alba-Delgado C, Llorca-Torralba M, Horrillo I, Ortega JE, Mico JA, Sánchez-Blázquez P, Meana JJ, Berrocoso E (2013) Chronic pain leads to concomitant noradrenergic impairment and mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry 73:54–62
Anand P, Kunnumakkara AB, Newman RA, Aggarwal BB (2007) Bioavailability of curcumin: problems and promises. Mol Pharm 4:807–818
Arnér S, Meyerson BA (1988) Lack of analgesic effect of opioids on neuropathic and idiopathic forms of pain. Pain 33:11–23
Arnow BA, Hunkeler EM, Blasey CM, Lee J, Constantino MJ, Fireman B, Kraemer HC, Dea R, Robinson R, Hayward C (2006) Comorbid depression, chronic pain, and disability in primary care. Psychosom Med 68:262–268
Atkinson JH, Slater MA, Williams RA, Zisook S, Patterson TL, Grant I, Wahlgren DR, Abramson I, Garfin SR (1998) A placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial of nortriptyline for chronic low back pain. Pain 76:287–296
Attal N, Cruccu G, Baron R, Haanpää M, Hansson P, Jensen TS, Nurmikko T (2010) EFNS guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain: revision. Eur J Neurol 17:1113–1123
Bair MJ, Robinson RL, Katon W, Kroenke K (2003) Depression and pain comorbidity: a literature review. Arch Intern Med 163:2433–2445
Benbouzid M, Gavériaux-Ruff C, Yalcin I, Waltisperger E, Tessier LH, Muller A, Kieffer BL, Freund-Mercier MJ, Barrot M (2008) Delta-opioid receptors are critical for tricyclic antidepressant treatment of neuropathic allodynia. Biol Psychiatry 63:633–636
Bennett GJ, Xie YK (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33:87–107
Berrocoso E, Mico JA (2009) Role of serotonin 5-HT1A receptors in the antidepressant-like effect and the antinociceptive effect of venlafaxine in mice. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12:61–71
Berrocoso E, Rojas-Corrales MO, Mico JA (2006) Differential role of 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors on the antinociceptive and antidepressant effect of tramadol in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 188:111–118
Boyce-Rustay JM, Palachick B, Hefner K, Chen YC, Karlsson RM, Millstein RA, Harvey-White J, Holmes A (2008) Desipramine potentiation of the acute depressant effects of ethanol: modulation by alpha2-adrenoreceptors and stress. Neuropharmacology 55:803–811
Brambilla P, Perez J, Barale F, Schettini G, Soares JC (2003) GABAergic dysfunction in mood disorders. Mol Psychiatry 8:721–737
De Souza MM, Pereira MA, Ardenghi JV, Mora TC, Bresciani LF, Yunes RA, Delle Monache F, Cechinel-Filho V (2009) Filicene obtained from Adiantum cuneatum interacts with the cholinergic, dopaminergic, glutamatergic, GABAergic, and tachykinergic systems to exert antinociceptive effect in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 93:40–46
Di Pierro F, Settembre R (2013) Safety and efficacy of an add-on therapy with curcumin phytosome and piperine and/or lipoic acid in subjects with a diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy treated with dexibuprofen. J Pain Res 6:497–503
Duarte FS, Lach G, Martins PR, Romeiro GA, de Lima TC (2008) Evidence for the involvement of the monoaminergic system in the antidepressant-like action of two 4-amine derivatives of 10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo [a, d] cycloheptane in mice evaluated in the tail suspension test. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:368–374
Gilhotra N, Dhingra D (2010) GABAergic and nitriergic modulation by curcumin for its antianxiety-like activity in mice. Brain Res 1352:167–175
Gonçalves L, Silva R, Pinto-Ribeiro F, Pêgo JM, Bessa JM, Pertovaara A, Sousa N, Almeida A (2008) Neuropathic pain is associated with depressive behaviour and induces neuroplasticity in the amygdala of the rat. Exp Neurol 213:48–56
Gustorff B, Dorner T, Likar R, Grisold W, Lawrence K, Schwarz F, Rieder A (2008) Prevalence of self-reported neuropathic pain and impact on quality of life: a prospective representative survey. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 52:132–136
Haley TJ, Mccormick WG (1957) Pharmacological effects produced by intracerebral injection of drugs in the conscious mouse. Br J Pharmacol Chemother 12:12–15
Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C, Joris J (1988) A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 32:77–88
Hasnie FS, Wallace VC, Hefner K, Holmes A, Rice AS (2007) Mechanical and cold hypersensitivity in nerve-injured C57BL/6J mice is not associated with fear-avoidance- and depression-related behaviour. Br J Anaesth 98:816–822
Hu B, Doods H, Treede RD, Ceci A (2009) Depression-like behaviour in rats with mononeuropathy is reduced by the CB2-selective agonist GW405833. Pain 143:206–212
Hylden JL, Wilcox GL (1980) Intrathecal morphine in mice: a new technique. Eur J Pharmacol 67:313–316
Jackson KC 2nd (2006) Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain. Pain Pract 6:27–33
Jesse CR, Wilhelm EA, Nogueira CW (2010) Depression-like behavior and mechanical allodynia are reduced by bis selenide treatment in mice with chronic constriction injury: a comparison with fluoxetine, amitriptyline, and bupropion. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 212:513–522
Johnston JP (1968) Some observations upon a new inhibitor of monoamine oxidase in brain tissue. Biochem Pharmacol 17:1285–1297
Kim H, Chen L, Lim G, Sung B, Wang S, McCabe MF, Rusanescu G, Yang L, Tian Y, Mao J (2012) Brain indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase contributes to the comorbidity of pain and depression. J Clin Invest 122:2940–2954
Kontinen VK, Kauppila T, Paananen S, Pertovaara A, Kalso E (1999) Behavioural measures of depression and anxiety in rats with spinal nerve ligation-induced neuropathy. Pain 80:341–346
Leo RJ (2005) Chronic pain and comorbid depression. Curr Treat Options Neurol 7:403–412
Luscher B, Shen Q, Sahir N (2011) The GABAergic deficit hypothesis of major depressive disorder. Mol Psychiatry 16:383–406
Magni G, Moreschi C, Rigatti-Luchini S, Merskey H (1994) Prospective study on the relationship between depressive symptoms and chronic musculoskeletal pain. Pain 56:289–297
Marchand F, Ardid D, Chapuy E, Alloui A, Jourdan D, Eschalier A (2003) Evidence for an involvement of supraspinal delta- and spinal mu-opioid receptors in the antihyperalgesic effect of chronically administered clomipramine in mononeuropathic rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 307:268–274
Max MB, Culnane M, Schafer SC, Gracely RH, Walther DJ, Smoller B, Dubner R (1987) Amitriptyline relieves diabetic neuropathy pain in patients with normal or depressed mood. Neurology 37:589–596
Micó JA, Ardid D, Berrocoso E, Eschalier A (2006) Antidepressants and pain. Trends Pharmacol Sci 27:348–354
Möhler H (2012) The GABA system in anxiety and depression and its therapeutic potential. Neuropharmacology 62:42–53
Nozaki C, Kamei J (2006) Possible involvement of opioidergic systems in the anti-nociceptive effect of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in sciatic nerve- injured mice. Eur J Pharmacol 552:99–104
Ohayon MM, Schatzberg AF (2003) Using chronic pain to predict depressive morbidity in the general population. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:39–47
Okamoto H, Voleti B, Banasr M, Sarhan M, Duric V, Girgenti MJ, Dileone RJ, Newton SS, Duman RS (2010) Wnt2 expression and signaling is increased by different classes of antidepressant treatments. Biol Psychiatry 68:521–527
Porsolt RD, Le Pichon M, Jalfre M (1977) Depression: a new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature 266:730–732
Radhakrishna Pillai G, Srivastava AS, Hassanein TI, Chauhan DP, Carrier E (2004) Induction of apoptosis in human lung cancer cells by curcumin. Cancer Lett 208:163–170
Reeta KH, Mehla J, Gupta YK (2010) Curcumin ameliorates cognitive dysfunction and oxidative damage in phenobarbitone and carbamazepine administered rats. Eur J Pharmacol 644:106–112
Sanacora G, Mason GF, Rothman DL, Krystal JH (2002) Increased occipital cortex GABA concentrations in depressed patients after therapy with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Am J Psychiatry 159:663–665
Savitz J, Lucki I, Drevets WC (2009) 5-HT1A receptor function in major depressive disorder. Prog Neurobiol 88:17–31
Shen Q, Lal R, Luellen BA, Earnheart JC, Andrews AM, Luscher B (2010) Gamma-aminobutyric acid-type A receptor deficits cause hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis hyperactivity and antidepressant drug sensitivity reminiscent of melancholic forms of depression. Biol Psychiatry 68:512–520
Shishodia S, Sethi G, Aggarwal BB (2005) Curcumin: getting back to the roots. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1056:206–217
Steru L, Chermat R, Thierry B, Simon P (1985) The tail suspension test: a new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 85:367–370
Suzuki T, Li YH, Mashimo T (2005) The antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic effects of neurotropin in mice with spinal nerve ligation. Anesth Analg 101:793–799
Suzuki T, Amata M, Sakaue G, Nishimura S, Inoue T, Shibata M, Mashimo T (2007) Experimental neuropathy in mice is associated with delayed behavioral changes related to anxiety and depression. Anesth Analg 104:1570–1577
Tanabe M, Tokuda Y, Takasu K, Ono K, Honda M, Ono H (2007) The synthetic TRH analogue taltirelin exerts modality-specific antinociceptive effects via distinct descending monoaminergic systems. Br J Pharmacol 150:403–414
Tyagarajan SK, Ghosh H, Yévenes GE, Nikonenko I, Ebeling C, Schwerdel C, Sidler C, Zeilhofer HU, Gerrits B, Muller D, Fritschy JM (2011) Regulation of GABAergic synapse formation and plasticity by GSK3beta-dependent phosphorylation of gephyrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:379–384
Viguier F, Michot B, Kayser V, Bernard JF, Vela JM, Hamon M, Bourgoin S (2012) GABA, but not opioids, mediates the anti-hyperalgesic effects of 5-HT7 receptor activation in rats suffering from neuropathic pain. Neuropharmacology 63:1093–1106
Villarinho JG, Pinheiro KD, Pinheiro FD, Oliveira SM, Machado P, Martins MA, Bonacorso HG, Zanatta N, Fachinetto R, Ferreira J (2013) The antinociceptive effect of reversible monoamine oxidase-A inhibitors in a mouse neuropathic pain model. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 44:136–142
Vo T, Rice AS, Dworkin RH (2009) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for neuropathic pain: how do we explain continued widespread use? Pain 143:169–171
Vollenweider I, Smith KS, Keist R, Rudolph U (2011) Antidepressant-like properties of α2-containing GABA(A) receptors. Behav Brain Res 217:77–80
Wang S, Tian Y, Song L, Lim G, Tan Y, You Z, Chen L, Mao J (2012) Exacerbated mechanical hyperalgesia in rats with genetically predisposed depressive behavior: role of melatonin and NMDA receptors. Pain 153:2448–2457
Xu Y, Ku BS, Yao HY, Lin YH, Ma X, Zhang YH, Li XJ (2005) The effects of curcumin on depressive-like behaviors in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 518:40–46
Xu Y, Ku B, Cui L, Li X, Barish PA, Foster TC, Ogle WO (2007) Curcumin reverses impaired hippocampal neurogenesis and increases serotonin receptor 1A mRNA and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in chronically stressed rats. Brain Res 1162:9–18
Yadav VS, Mishra KP, Singh DP, Mehrotra S, Singh VK (2005) Immunomodulatory effects of curcumin. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 27:485–497
Yalcin I, Tessier LH, Petit-Demoulière N, Doridot S, Hein L, Freund-Mercier MJ, Barrot M (2009) Beta2-adrenoceptors are essential for desipramine, venlafaxine or reboxetine action in neuropathic pain. Neurobiol Dis 33:386–394
Yalcin I, Bohren Y, Waltisperger E, Sage-Ciocca D, Yin JC, Freund-Mercier MJ, Barrot M (2011) A time-dependent history of mood disorders in a murine model of neuropathic pain. Biol Psychiatry 70:946–953
Ye ZY, Zhou KQ, Xu TL, Zhou JN (2008) Fluoxetine potentiates GABAergic IPSCs in rat hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett 442:24–29
Zhao X, Xu Y, Zhao Q, Chen CR, Liu AM, Huang ZL (2012) Curcumin exerts antinociceptive effects in a mouse model of neuropathic pain: descending monoamine system and opioid receptors are differentially involved. Neuropharmacology 62:843–854
Zhen L, Zhu J, Zhao X, Huang W, An Y, Li S, Du X, Lin M, Wang Q, Xu Y, Pan J (2012) The antidepressant-like effect of fisetin involves the serotonergic and noradrenergic system. Behav Brain Res 228:359–366
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the K.C. Wong Magna Fund in Ningbo University, National Natural Science Foundation of China (81201050), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY12H09002), and Innovative Research Team of Ningbo (2009B21002).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Wang, C., Zhang, JF. et al. Chronic curcumin treatment normalizes depression-like behaviors in mice with mononeuropathy: involvement of supraspinal serotonergic system and GABAA receptor. Psychopharmacology 231, 2171–2187 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3368-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3368-2