Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to explore the influence of a half-course tourniquet strategy on the peri-operative blood loss and early functional recovery in primary total knee arthroplasty.
Methods
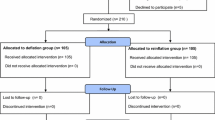
A prospective clinical randomised controlled study was carried out in which 64 patients were equally divided into two groups: half-course group and whole-course group. A series of indicators were observed and recorded. These included operation time, peri-operative blood loss, visual analogue scale (VAS) score of the thigh or knee, limb swelling index, rehabilitation progress and occurrence of deep venous thrombosis cases.
Results
There was no significant difference in operation time between the two groups. The intra-operative blood loss was slightly more in the half-course group, while the difference was not significant. The post-operative blood loss and calculated blood loss were less in the half-course group and the difference was significant. The thigh VAS score, limb swelling and time intervals required for patients to achieve straight leg raises and 90° of knee flexion in the half-course group were better than in the whole-course group. No case of symptomatic deep venous thrombosis happened in this study, while occult incidence of deep venous thrombosis happened in both groups, but no significant difference between the groups was confirmed.
Conclusions
The half-course tourniquet strategy could decrease the total peri-operative blood loss in primary total knee arthroplasty. It was beneficial in helping patients to achieve earlier functional recovery by improving the pain experience and limb swelling early in the post-operative period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vandenbussche E, Duranthon LD, Couturier M, Pidhorz L, Augereau B (2002) The effect of tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 26(5):306–309. doi:10.1007/s00264-002-0360-6
Matziolis D, Perka C, Hube R, Matziolis G (2011) Influence of tourniquet ischemia on perioperative blood loss after total knee arthroplasty. Orthopade 40(2):178–182. doi:10.1007/s00132-010-1727-9
Stroh DA, Johnson AJ, Mont MA, Bonutti PM (2011) Excellent clinical outcomes in total knee arthroplasty performed without a tourniquet. Surg Technol Int XXI:189–193
Tai TW, Chang CW, Lai KA, Lin CJ, Yang CY (2012) Effects of tourniquet use on blood loss and soft-tissue damage in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am 94(24):2209–2215. doi:10.2106/jbjs.k.00813
Abdel-Salam A, Eyres KS (1995) Effects of tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty. A prospective randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 77(2):250–253
Reikerås O, Clementsen T (2009) Time course of thrombosis and fibrinolysis in total knee arthroplasty with tourniquet application. Local versus systemic activations. J Thromb Thrombolysis 28(4):425–428. doi:10.1007/s11239-008-0299-6
Wauke K, Nagashima M, Kato N, Ogawa R, Yoshino S (2002) Comparative study between thromboembolism and total knee arthroplasty with or without tourniquet in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 122(8):442–446. doi:10.1007/s00402-002-0404-9
Tetro AM, Rudan JF (2001) The effects of a pneumatic tourniquet on blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Can J Surg 44(1):33–38
Li B, Wen Y, Wu H, Qian Q, Lin X, Zhao H (2009) The effect of tourniquet use on hidden blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 33(5):1263–1268. doi:10.1007/s00264-008-0647-3
Turner L, Shamseer L, Altman DG, Weeks L, Peters J, Kober T, Dias S, Schulz KF, Plint AC, Moher D (2012) Consolidated standards of reporting trials (CONSORT) and the completeness of reporting of randomised controlled trials (RCTs) published in medical journals. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 11:MR000030. doi:10.1002/14651858.MR000030.pub2
Gross JB (1983) Estimating allowable blood loss: corrected for dilution. Anesthesiology 58(3):277–280
Sehat KR, Evans RL, Newman JH (2004) Hidden blood loss following hip and knee arthroplasty. Correct management of blood loss should take hidden loss into account. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86(4):561–565
Sehat KR, Evans R, Newman JH (2000) How much blood is really lost in total knee arthroplasty? Correct blood loss management should take hidden loss into account. Knee 7(3):151–155
Zhang FJ, Xiao Y, Liu YB, Tian X, Gao ZG (2010) Clinical effects of applying a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty on blood loss. Chin Med J 123(21):3030–3033
Ledin H, Aspenberg P, Good L (2012) Tourniquet use in total knee replacement does not improve fixation, but appears to reduce final range of motion. Acta Orthop 83(5):499–503. doi:10.3109/17453674.2012.727078
Harvey EJ, Leclerc J, Brooks CE, Burke DL (1997) Effect of tourniquet use on blood loss and incidence of deep vein thrombosis in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 12(3):291–296
Schuh A, Hausel M, Salminen S (2003) Effect of tourniquet use on blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Zentralbl Chir 128(10):866–870. doi:10.1055/s-2003-44339
Ishii Y, Matsuda Y (2005) Effect of the timing of tourniquet release on perioperative blood loss associated with cementless total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study. J Arthroplasty 20(8):977–983. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2005.01.012
Yavarikia A, Amjad GG, Davoudpour K (2010) The influence of tourniquet use and timing of its release on blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Pak J Biol Sci 13(5):249–252
Dutton T, De-Souza R, Parsons N, Costa ML (2012) The timing of tourniquet release and ‘retransfusion’ drains in total knee arthroplasty: a stratified randomised pilot investigation. Knee 19(3):190–192. doi:10.1016/j.knee.2011.02.013
Mittal R, Ko V, Adie S, Naylor J, Dave J, Dave C, Harris IA, Hackett D, Ngo D, Dietsch S (2012) Tourniquet application only during cement fixation in total knee arthroplasty: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial. ANZ J Surg 82(6):428–433. doi:10.1111/j.1445-2197.2012.06083.x
Abbas K, Raza H, Umer M, Hafeez K (2013) Effect of early release of tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 23(8):562–565. doi:08.2013/jcpsp.562565
Kvederas G, Porvaneckas N, Andrijauskas A, Svensen CH, Ivaskevicius J, Mazunaitis J, Marmaite U, Andrijauskas P (2012) A randomized double-blind clinical trial of tourniquet application strategies for total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-012-2221-1
Westman B, Weidenhielm L, Rooyackers O, Fredriksson K, Wernerman J, Hammarqvist F (2007) Knee replacement surgery as a human clinical model of the effects of ischaemia/reperfusion upon skeletal muscle. Clin Sci (Lond) 113(7):313–318. doi:10.1042/cs20070025
Mas E, Barden AE, Corcoran TB, Phillips M, Roberts LJ 2nd, Mori TA (2011) Effects of spinal or general anesthesia on F(2)-isoprostanes and isofurans during ischemia/reperfusion of the leg in patients undergoing knee replacement surgery. Free Radic Biol Med 50(9):1171–1176. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.01.021
Hori K, Tsujii M, Iino T, Satonaka H, Uemura T, Akeda K, Hasegawa M, Uchida A, Sudo A (2013) Protective effect of edaravone for tourniquet-induced ischemia-reperfusion injury on skeletal muscle in murine hindlimb. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 14:113. doi:10.1186/1471-2474-14-113
Iltar S, Kilinc CY, Alemdaroglu KB, Ozcan S, Aydogan NH, Surer H, Kilinc AS (2013) Does the method of expression of venous blood affect ischaemia/reperfusion damage in tourniquet use? An experimental study on rabbits. Injury 44(11):1493–1497. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2013.02.010
Bao H, Wang J, Cai Y, Chu X, Lv C, Dong P (2011) Tourniquet ischemia reperfusion injury after total knee arthroplasty in clinical research. Chin J Orthop Trauma 13(3):242–246. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-7600.2011.03.011
Barwell J, Anderson G, Hassan A, Rawlings I (1997) The effects of early tourniquet release during total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized double-blind study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 79(2):265–268
Wakankar HM, Nicholl JE, Koka R, D’Arcy JC (1999) The tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty. A prospective, randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 81(1):30–33
Berman AT, Parmet JL, Harding SP, Israelite CL, Chandrasekaran K, Horrow JC, Singer R, Rosenberg H (1998) Emboli observed with use of transesophageal echocardiography immediately after tourniquet release during total knee arthroplasty with cement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 80(3):389–396
Fukuda A, Hasegawa M, Kato K, Shi D, Sudo A, Uchida A (2007) Effect of tourniquet application on deep vein thrombosis after total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 127(8):671–675. doi:10.1007/s00402-006-0244-0
Kato N, Nakanishi K, Yoshino S, Ogawa R (2002) Abnormal echogenic findings detected by transesophageal echocardiography and cardiorespiratory impairment during total knee arthroplasty with tourniquet. Anesthesiology 97(5):1123–1128
Hernandez AJ, de Almeida AM, Fávaro E, Sguizzato GT (2012) The influence of tourniquet use and operative time on the incidence of deep vein thrombosis in total knee arthroplasty. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 67(9):1053–1057
Aggarwal AK, Shashikanth VS, Marwaha N (2013) Platelet-rich plasma prevents blood loss and pain and enhances early functional outcome after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomised controlled study. Int Orthop. doi:10.1007/s00264-013-2136-6
Iwai T, Tsuji S, Tomita T, Sugamoto K, Hideki Y, Hamada M (2013) Repeat-dose intravenous tranexamic acid further decreases blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 37(3):441–445. doi:10.1007/s00264-013-1787-7
Sasaki H, Ishida K, Shibanuma N, Tei K, Tateishi H, Toda A, Yamashiro Y, Matsumoto T, Kuroda R, Kurosaka M (2013) Retrospective comparison of three thromboprophylaxis agents, edoxaban, fondaparinux, and enoxaparin, for preventing venous thromboembolism in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. doi:10.1007/s00264-013-2132-x
Schousboe JT, Brown GA (2013) Cost-effectiveness of low-molecular-weight heparin compared with aspirin for prophylaxis against venous thromboembolism after total joint arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 95(14):1256–1264. doi:10.2106/jbjs.l.00400
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Sen Chen and JianPing Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Li, J., Peng, H. et al. The influence of a half-course tourniquet strategy on peri-operative blood loss and early functional recovery in primary total knee arthroplasty. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 38, 355–359 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-013-2177-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-013-2177-x