Abstract
Background
The International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) concluded that “there is currently no reason to doubt that the reduction of dependent survival or death after endovascular coiling seen in all patients in the ISAT cohort should not be valid in the elderly”. We feel that this generalization requires further investigation to assess its validity.
Methods
We studied the impact of treatment era and independent risk factors for outcome in 179 consecutive elderly (≥70 years) aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH) patients admitted to Kuopio University Hospital either between 1983 and 1992 (Era I, n = 56), prior to the introduction of endovascular management, or between 1995 and 2004 (Era II, n = 123) when the endovascular treatment was established at our institute. Altogether 150 patients underwent occlusive aneurysm treatment, 47 clipping in the Era I as against 49 clipping, 49 endovascular therapy, and five combination therapy in the Era II.
Results
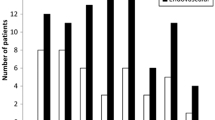
The 12-month survival (n = 179) did not improve from the Era I to the Era II. The proportion of good outcome (GOS IV–V) after occlusive therapy (n = 150) was equal in the Era I and Era II (n = 27/47; 57% vs. n = 56/103; 54%). In multivariate logistic regression analysis, independent predictors of poor outcome were age, poor grade (Hunt&Hess IV–V), hydrocephalus, hypertension, and intraventricular hemorrhage, but not the mode of occlusive therapy (microsurgical vs. endovascular)
Conclusion
Clinical severity of the SAH was the most significant predictor of outcome. Integration of coil treatment in clinical practice has not improved the overall outcome of aSAH in the elderly at our institute.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai Y, Spelle L, Wang H, Piotin M, Mounayer C, Vanzin JR, Moret J (2005) Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms in the elderly: single-center experience in 63 consecutive patients. Neurosurgery 57:1096–1102
Chung RY, Carter BS, Norbash A, Budzik R, Putnam C, Ogilvy CS (2000) Management outcomes for ruptured and unruptured aneurysms in the elderly. Neurosurgery 47:827–832
Fisher CM, Kistler JP, Davis JM (1980) Relation of cerebral vasospasm to subarachnoid hemorrhage visualized by computerized tomographic scanning. Neurosurgery 6:1–9
Fridriksson SM, Hillman J, Saveland H, Brandt L (1995) Intracranial aneurysm surgery in the 8th and 9th decades of life: impact on population-based management outcome. Neurosurgery 37:627–631
Horiuchi T, Tanaka Y, Hongo K (2005) Surgical treatment for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in the 8th and 9th decades of life. Neurosurgery 56:469–475
Hunt WE, Hess RM (1968) Surgical risk as related to time of intervention in the repair of intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg 28:14–20
Inagawa T (1993) Management outcome in the elderly patient following subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 78:554–561
Jain R, Deveikis J, Thompson BG (2004) Endovascular management of poor-grade aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in the geriatric population. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:596–600
Jennet B, Bond M (1975) Assesment of outcome after severe brain damage: a practical scale. Lancet 1:480–484
Koivisto T, Vanninen R, Hurskainen H, Saari T, Hernesniemi J, Vapalahti M (2000) Outcomes of early endovascular versus surgical treatment of ruptured cerebral aneurysms: a prospective randomized study. Stroke 31:2369–2377
Laidlaw JD, Siu KH (2002) Aggressive surgical treatment of elderly patients following subarachnoid haemorrhage: management outcome results. J Clin Neurosci 9:404–410
Lanzino G, Kassell NF, Germanson TP, Kongable GL, Truskowski LL, Torner JC, Jane JA (1996) Age and outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: why do older patients fare worse? J Neurosurg 85:410–418
Lubicz B, Leclerc X, Gauvrit JY, Lejeune JP, Pruvo JP (2004) Endovascular treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms in elderly people. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:592–595
Molyneux A, Kerr R, Stratton I, Sandercock P, Clarke M, Shrimpton J, Holman R (2002) International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised trial. Lancet 360:1267–1274
Molyneux AJ, Kerr RS, Yu LM, Clarke M, Sneade M, Yarnold JA, Sandercock P (2005) International subarachnoid aneurysm trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised comparison of effects on survival, dependency, seizures, rebleeding, subgroups, and aneurysm occlusion. Lancet 366:809–817
Nieuwkamp DJ, Rinkel GJ, Silva R, Greebe P, Schokking DA, Ferro JM (2006) Subarachnoid haemorrhage in patients > or =75 years: clinical course, treatment and outcome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77:933–937
Nilsson OG, Saveland H, Ramgren B, Cronqvist M, Brandt L (2005) Impact of coil embolization on overall management and outcome of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 57:216–224
O’Kelly CJ, Kulkarni AV, Austin PC, Wallace MC, Urbach D (2009) The impact of therapeutic modality on outcomes following repair of ruptured intracranial aneurysms: an administrative data analysis. J Neurosurg. doi:10.3171/2009.9.JNS081645
Qu F, Aiyagari V, Cross DT 3rd, Dacey RG Jr, Diringer MN (2004) Untreated subarachnoid hemorrhage: who, why, and when? J Neurosurg 100:244–249
Ryttlefors M, Enblad P, Kerr RS, Molyneux AJ (2008) International subarachnoid aneurysm trial of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling: subgroup analysis of 278 elderly patients. Stroke 39:2720–2726
Sacco RL, Wolf PA, Bharucha NE, Meeks SL, Kannel WB, Charette LJ, McNamara PM, Palmer EP, D'Agostino R (1984) Subarachnoid and intracerebral hemorrhage: natural history, prognosis, and precursive factors in the Framingham Study. Neurology 34:847–854
Sedat J, Dib M, Lonjon M, Litrico S, Von Langsdorf D, Fontaine D, Paquis P (2002) Endovascular treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms in patients aged 65 years and older: follow-up of 52 patients after 1 year. Stroke 33:2620–2625
Statistics of Finland: Population. http://www.tilastokeskus.fi/tup/suoluk/suoluk_vaesto_en.htlm. Updated April 3, 2009. Accessed April 3, 2009
Suarez JI, Tarr RW, Selman WR (2006) Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. N Engl J Med 354:387–396
van Gijn J, Kerr RS, Rinkel GJ (2007) Subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet 369:306–318
Vanninen R, Koivisto T, Saari T, Hernesniemi J, Vapalahti M (1999) Ruptured intracranial aneurysms: acute endovascular treatment with electrolytically detachable coils—a prospective randomized study. Radiology 211:325–336
Wang MC, Elliott JP, Le Roux PD (2004) Subarachnoid hemorrhage and cerebral aneurysms in elderly people. In: Le Roux PD, Winn HR, Newell DW (eds) Management of Cerebral Aneurysms. Philadelphia, Saunders, pp 409–419
Yamashita K, Kashiwagi S, Kato S, Takasago T, Ito H (1997) Cerebral aneurysms in the elderly in Yamaguchi, Japan. Analysis of the Yamaguchi Data Bank of Cerebral Aneurysm from 1985 to 1995. Stroke 28:1926–1931
Grant information/other acknowledgments
This research has been supported by grants from the Kuopio University, the Finnish Cultural Foundation and the Finnish Medical Foundation.
We gratefully acknowledge Nick Hayward, BA (Hons, Cantab) MSc, (A I Virtanen Institute, University of Kuopio, Kuopio, Finland) for his suggestions regarding the language of the manuscript.
We wish to thank Vesa Kiviniemi, MSc (IT Center, Statistical and Mathematical Services, University of Kuopio, Kuopio, Finland) for the help with the statistical analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karamanakos, P.N., Koivisto, T., Vanninen, R. et al. The impact of endovascular management on the outcome of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in the elderly in Eastern Finland. Acta Neurochir 152, 1493–1502 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0714-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0714-6