Abstract
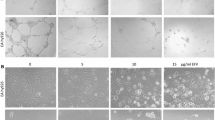
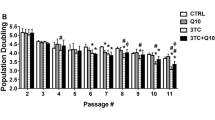
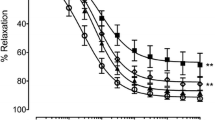
Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) has significantly improved the prognosis of HIV-1-infected patients but is associated with significant side effects such as diabetes, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular complications. Oxidative stress can disrupt endothelial homeostasis by dysregulating the balance between pro- and antiatherogenic factors. We hypothesized that chronic exposure to HAART results in endothelial oxidative stress and activation of mononuclear cell recruitment, an early event in atherosclerosis. We studied the effects of HAART drug combinations, consisting of zidovudine, a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor; efavirenz, a nonnucleosiee reverse transcriptase inhibitor; and either of the two protease inhibitors (PIs), indinavir or nelfinavir, on human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) by monitoring the following parameters: (1) generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), (2) mononuclear cell (Jurkat or U-937) adhesion, and (3) expression of cell adhesion molecules (CAMs). HAART exposure increased ROS formation in HAECs. Exposure to Pls alone and in HAART combinations increased mononuclear cell adhesion to HAECs in a concentration-dependent manner. Mononuclear cell adhesion to HAART-exposed HAECs was significantly enhanced following acute (24-h) exposure to the inflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α or interleukin (IL)-1β and was suppressed by the antioxidants N-acetylcysteine and glutathione. Exposure to HAART increased intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) gene expression and concomitant exposure to TNF-α, further increased ICAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), and endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule cell surface protein levels. These studies indicate that chronic HAART exposure increases oxidative stress in endothelial cells and induces mononuclear cell recruitment, which may eventually precipitate the cardiovascular disease observed in HIV-1+ individuals on antiretroviral therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carr, A. (2003). Cardiovascular risk factors in HIV-infected patients. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 34:S73-S78.
Barthelemy, O., Escaut, L., Vayre, F., Gallet, B., Pulik, M., Heliore, F., et al. (2002). Acute coronary syndromes in patients treated with HIV protease inhibitors. Presse. Med. 31:343–348.
Carr, A. (2003). HIV lipodystrophy: risk factors, pathogenesis, diagnosis and management. AIDS. 17:S141-S148.
Rubanyi, G. M. (1993). The role of endothelium in cardiovascular homeostasis and diseases. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 22:S1-S14.
Gonzalez-Amaro, R., Diaz-Gonzalez, F., and Sanchez-Madrid, F. (1988). Adhesion molecules in inflammatory diseases. Drugs. 56:977–988.
Collins, T., Read, M. A., Neish, A. S., Whitley, M.Z., Thanos, D., and Maniatis, T. (1995). Transcriptional regulation of endothelial cell adhesion molecules: NF-kappa B and cytokine-inducible enhancers. FASEB J. 9:899–909.
Walia, M. Samson, S. E., Schmidt, T., Best, K., Kwan, C.Y., and Grover, A. K. (2003). Effects of peroxynitrite on pig coronary artery smooth muscle. Cell Calcium. 34:69–74.
Moskowitz, R. and Kukin, M. (1999). Oxidative stress and congestive heart failure. Congest. Heart Fail. 5:153–163.
Chen, K.H, Reece, L.M., and Leary, J.F (1999). Mitochondrial glutathione modulates TNF-alpha-induced endothelial cell dysfunction. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 27:100–109.
Chen, X.L., Zhang, Q., Zhao, R., and Medford, R.M. (2004). Superoxide, H2O2 and iron are requred for TNFalpha-induced MCP-1 gene expression in endothelial cells: role of Rac 1 and NADPH oxidase. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 286:H1001-H1007.
Gupta, B. and Ghosh, B. (1999). Curcuma longa inhibits TNF-alpha induced expression of adhesion molecules on human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 21:745–757.
Mondal, D. and Agrawal, K.C. (1996). Effect of HIV type 1 Tat protein on butyric acid-induced differentiation in a hematopoietic progenioor cell line. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 12:1529–1536.
Barbaro, G. (2003). HIV infection, highly active antiretroviral therapy and the cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc. Res. 60:87–95.
Eissner, G., Kolch, W., Mischak, H., Bornkamm, G.W., and Holler, E. (1994). Differential role of protein kinase C in cytokine induced lymphocyte-endothelium interaction in vitro. Scand. J. Immunol. 40:395–402.
Deisher, T. A., Haddix, T.L., Montgomery, K. F., Pohlman, T. H., Kaushansky, K., and Harlan, J. M. (1993). The role of protein kinase C in the induction of VCAM-1 expression on human umbilical vein endothelial cells. FEBS Lett. 331:285–290.
Scott-Algara, D., Vuillier, F., Marasescu, M., de Saint Martin, J., and Dighiero, G. (1991). Serum levels of IL-2, IL-1α, TNF-α, and soluble receptor of IL-2 in HIV-1-infected patients. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 7:381–386.
Bilello, J. A., Stellrecht, K., Drusano, G. L., and Stein, D. S. (1996). Soluble tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor type II (sTNF-αRII) correlates with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) RNA copy number in HIV-infected patients. J. Infect. Dis. 173:464–467.
Medrano, F. J., Rey, C., Leal, M., Canavate, C., Rubio, A., Sanchez-Quijano, A., et al. (1998). Dynamics of serum cytokines in patients with visceral leishmaniasis and HIV-1 co-infection. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 114:403–407.
Jialal, I., Devaraj, S., and Venugopal, S.K. (2002). Oxidative stress, inflammation, and diabetic vasculopathies: the role of alpha tocopherol therapy. Free Radic. Res. 36: 1331–1336.
Hsiai, T.K., Cho, S.K., Wong, P.K., Ing, M., Salazar, A., Sevanian, A., et al. (2003). Monocyte recruitment to endothelial cells in response to oscillatory shear stress. FASEB J. 17:1648–1657.
Mondal, D., Larussa, V.F., and Agrawal, K.C. (2001). Synergistic antiadipogenic effects of HIV type 1 protease inhibitors with tumor necrosis factor alpha: suppression of extracellular insulin action mediated by extracellular matrix-degrading proteases. AIDS Res. Hum Retroviruses 17:1569–1584.
Caron, M., Auclair, M., Sterlingot, H., Kornprobst, M., and Capeau, J. (2003). Some HIV protease inhibitors alter lamin A/C maturation and stability, SREBP-1 nuclear localization and adipocyte differentiation. AIDS 17:2437–2444.
Blankenberg, S., Barbaux, S., and Tiret, L. (2003). Adhesion molecules and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 170: 191–203.
Alcoba, M., Cuevas, M.J., Perez-Simon, M.R., Mostaza, J.L., Ortega, L., Ortiz de Urbina, J., et al. (2003). Assessment of adherence to triple antiretroviral treatment including indinavir: role of the determination of plasma levels of indinavir. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 33:253–258.
Calza, L., Manfredi, R., and Chiodo, F. (2003). Hyperlipidaemia in patients with HIV-1 infection receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy: epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical course and management. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 22:89–99.
AIDS Info. http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/guidelines. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-infected adults and adolescents. July 14, 2003; 55.
Zahler, S., Kupatt, C., and Becker, B. F. (2000). Endothione preconditioning by transient oxidative stress reduces inflammatory responses of cultured endothelial cells to TNF-alpha. FASEB J. 14:555–564.
Chaudiere, J., Moutet, M., and D’Alessio, P. (1995). Antioxidants and anti-inflammatory protection of vascular endothelial cells by new synthetic mimics of glutathione peroxidase. C R Seances Soc. Biol. Fil. 189:861–882.
Hulgan, T., Morrow, J., D’Aquila, R. T., Raffanti S., Morgan M., Rebeiro, P., et al. (2003). Oxidant stress is increased during treatment of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 37:1711–1717.
Jareno, E.J., Roma, J., Romero, B., Marin, N., Muriach, M., Johsen, S., et al. (2002). Serum malondialdehyde correlates with therapeutic efficiency of high activity antiretroviral therapies (HAART) in HIV-1 infected children. Free Radic. Res. 36:341–344.
Aukrust, P., Muller, F., Svardal, A. M., Ueland, T., Berge, R.K., and Froland, S. S. (2003). Disturbed glutathione metabolism and decreased levels in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients during highly active antiretroviral therapy—potential immuno-modulatory effects of antioxidants. J. Infect. Dis. 188:232–238.
Capaldini, L. (1997). Protease inhibitors’ metabolic side effects: cholesterol, triglycerides, blood sugar, and “Crix belly”. Interview with Lisa Capaldini, M.D. Interview by John S. James. AIDS Treat. News 277:1–4.
Calista, D. and Boschini, A. (2000). Cutaneous side effects induced by indinavir. Eur. J. Dermatol. 10:292–296.
Birdsall, H. H., Siwak, E. B., Trial, J., Rodriguez-Barradas, M., White, A. C., Jr., Wietgrefe, S., et al. (2002). Transendothelial migration of leukocytes carrying infectious HIV-1: an indicator of adverse prognosis. AIDS 16:5–12.
Arroyo, A. G., Garcia-Vicuna, R., Marazuela, M., Yednock, T.A., Gonzalez-Amaro, R., and Sanchez-Madrid, F. (1995). Expression and functional significance of an activation-dependent eptiope of the beta 1 integrins in chronic inflammatory diseases. Eur. J. Immunol. 25:1720–1728.
Kalogeris, T. J., Kevil, C. G., Laroux, F. S., Coe, L. L., Phifer, T. J., and Alexander, J. S. (1999). Differential mono-cyte adhesion and adhesion molecule expression in venous and arterial endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 276: L9-L19.
Kvietys, P.R. and Granger, D.N. (1997). Endothelial cell monolayers as a tool for studying microvascular pathophysiology. Am. J. Physiol. 273:G1189-G1199. (Review).
Panes, J., Perry, M.A., Anderson, D.C., Manning, A., Leone, B., Cepinskas, G., et al. (1995). Regional differences in constitutive and induced ICAM-1 expression in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. 269:H1955-H1964.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mondal, D., Pradhan, L., Ali, M. et al. HAART drugs induce oxidative stress in human endothelial cells and increase endothelial recruitment of mononuclear cells. Cardiovasc Toxicol 4, 287–302 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/CT:4:3:287
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/CT:4:3:287